Set up jupyter notebook with docker-compose and tensorflow
Using single command to set up whole environment that is isolated and self-contained is very useful not only for machine learning projects. Docker together with docker-compose can do it with very little effort from our side.
Here is how to create simple setup for environment with tensorflow gpu, python and jupyter notebooks using docker.
- Create new directory
docker_setup - In this directory create new file with name
Dockerfilewithout extension and fill it with line:FROM tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu-py3This is almost the simplest Dockerfile you can write. This will build a container from tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu-py3 image without adding anything extra to it.
- Create file
docker-compose.ymland fill it with this content:version: '2.3' services: tensor: build: ./ runtime: nvidia environment: - NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all volumes: - ./src:/notebooks ports: - 8888:8888This translates to the following:
- Create 1 service called “tensor”
- Build docker image from current directory
- Use nvidia runtime (nvidia-docker)
- Make all nvidia devices visible to the environment
- Map “src” directory to “notebooks” directory that’s inside the docker container
- Forward port 8888 to port 8888 in the container
-
We are missing “src” folder so let’s create it among Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml. Our jupyter notebooks will be stored there.
-
Run
sudo docker-compose upcommand inside docker_setup directory. Jupyter notebook should be hosted locally on port 8888: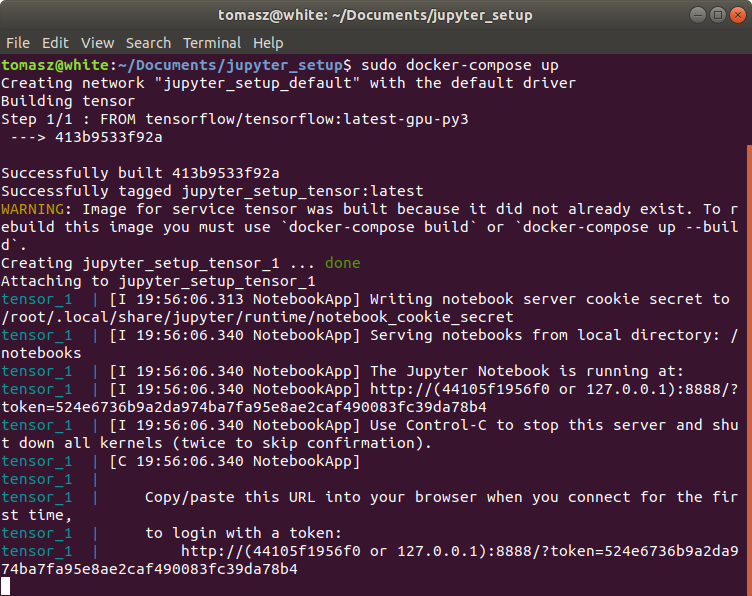
-
Browse 127.0.0.1:8888/?token=
your token: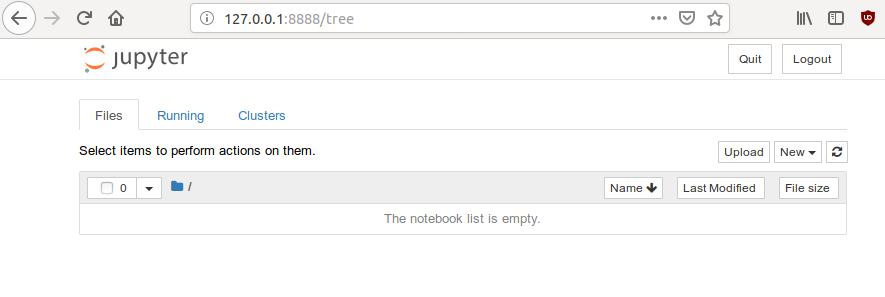
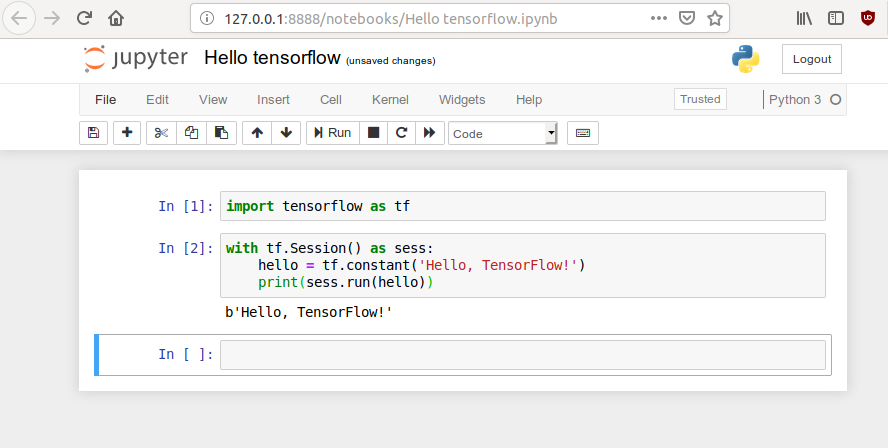
- You can test if tensorflow is running by creating simple script in new notebook:
In case of any problems, whole solution is hosted on github: https://github.com/sikora507/docker-tensorflow-gpu-jupyter